Shiken: JALT Testing & Evaluation SIG Newsletter
Vol. 12 No. 2. Apr. 2008. (p. 38 - 43) [ISSN 1881-5537]
Effect size and eta squared |
 James Dean Brown University of Hawai'i at Manoa |
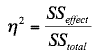

| Source | SS | df | MS | F | p | eta2 | Power |
| Anxiety | 0.08 | 1 | 0.08 | 0.02 | 0.90 | 0.0012 | 0.05 |
| Tension | 2.08 | 1 | 2.08 | 0.38 | 0.55 | 0.0324 | 0.09 |
| Anxiety x Tension | 18.75 | 1 | 18.75 | 3.46 | 0.10 | 0.2919 | 0.37 |
| Error | 43.33 | 8 | 5.42 | 0.6745 | |||
| Total | 64.24 | 12 |
[ p. 38 ]
| Anxiety | Tension | M | SD | N |
| 1 | 1 | 8.67 | 3.06 | 3 |
| 2 | 7.00 | 2.65 | 3 | |
| 2 | 1 | 6.00 | 2.00 | 3 |
| 2 | 9.33 | 1.16 | 3 |

[ p. 39 ]

| "One problem with eta2 is that the magnitude of eta2 for each particular effect depends to some degree on the significance and number of other effects in the design" |
[ p. 40 ]

| Source | SS | df | MS | F | p |
| Between Subjects | |||||
| 158.372 | 9 | 17.597 | 9.703 | 0.00 | |
| 3068.553 | 1692 | 1.814 | |||
| Within Subjects | |||||
| Topic Type | 0.344 | 1 | 0.344 | 0.194 | 0.66 |
| 137.572 | 9 | 15.286 | 8.611 | 0.00 | |
| 3003.548 | 1692 | 1.775 | |||
| Source | SS | df | MS | F | p | Partial eta2 |
| Between Subjects | ||||||
| 158.372 | 9 | 17.597 | 9.703 | 0.00 | 0.0490 | |
| 3068.553 | 1692 | 1.814 | ||||
| Within Subjects | ||||||
| Topic Type | 0.344 | 1 | 0.344 | 0.194 | 0.66 | 0.0490 |
| 137.572 | 9 | 15.286 | 8.611 | 0.00 | 0.0438 | |
| 3003.548 | 1692 | 1.775 | ||||
[ p. 41 ]

| "Reporting the traditional ANOVA source table (with SS, df, MS, F, and p) and discussing the associated significance levels isn't the end of the study; it's just the beginning . . ." |
[ p. 42 ]
Brown, J. D. (2007). Statistics Corner. Questions and answers about language testing statistics: Sample size and power. Shiken: JALT Testing & Evaluation SIG Newsletter, 11(1), 31-35. Also retrieved from the World Wide Web at http://jalt.org/test/bro_25.htm| Where to Submit Questions: |
| Please submit questions for this column to the following address: |
|
JD Brown Department of Second Language Studies University of Hawai'i at Manoa 1890 East-West Road Honolulu, HI 96822 USA |
[ p. 43 ]