Shiken: JALT Testing & Evaluation SIG Newsletter
Vol. 14 No. 1. March 2010. (pp. 24 - 35) [ISSN 1881-5537]
|
Possible answers for the nine questions about testing/assessment which were in the March 2010 issue of this newsletter appear below. |
![]()
[ p. 26 ]
|
Further reading: Carson, C. (n.d.) The effective use of effect size indices in institutional research. Retrieved March 14, 2010 from http://www.keene.edu/ir/effect_size.pdf Cohen, J. (1988). Statistical power for the behavioral sciences (2nd ed.). Hillsdale, NJ: Erlbaum. Cortina, J. M. & Nouri, H. (2000). Effect size for ANOVA designs. Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage Publications. Effect Size. (2010, March 10). Wikipedia: The Free Encyclopedia. Retrieved March 9, 2010 from http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Effect_size Ferguson, C. J. (2009). An Effect Size Primer: A Guide for Clinicians and Researchers. Professional Psychology: Research and Practice, 40 (5) 532 - 538. DOI: 10.1037/a0015808 Graziano, A. M. & Raulin, M. L. (2000). Online Glossary to Research Methods: A Process of Inquiry (4th Edition). Retrieved March 11, 2010 from http://web.squ.edu.om/med-Lib/MED_CD/E_CDs/SPSS/glossary/glosse.htm Hedges, L. V. (1981). Distribution Theory for Glass's Estimator of Effect size and Related Estimators. Journal of Educational and Behavioral Statistics, 6 (2) 107-128. DOI: 10.3102/10769986006002107 Hedges, L. V., & Olkin, I. (1985). Statistical methods for meta-analysis. San Diego, CA: Academic Press. Levine, T. R. & Hullett, C. R. (2002). Eta Squared, Partial Eta Squared, and Misreporting of Effect Size in Communication Research. Human Communication Research, 28 (4) 612-625. Retrieved March 14, 2010 from www.informaworld.com/index/912219870.pdf Morris, S. B. (2008). Estimating Effect Sizes From Pretest-Posttest-Control Group Designs. Organizational Research Methods, 11 (2) 364-386. DOI: 10.1177/1094428106291059 Rosnow, R. L., Rosenthal R., & Rubin, D. B. (2000). Contrasts and correlations in effect-size estimation. Psychological Science, 11 (6) 446-453. DOI: 10.1111/1467-9280.00287 U.S. Department of Education Institute of Education Science & What Works Clearinghouse. (2008). WWC Standards (Version 1): Improvement Index. Retrieved March 9, 2010 from http://ies.ed.gov/ncee/wwc/references/iDocViewer/Doc.aspx?docId=20&tocId=4 Valentine, J. C. & Cooper, H. (2003). Effect size substantive interpretation guidelines: Issues in the interpretation of effect sizes. Washington, DC: What Works Clearinghouse. Retrieved March 14, 2010 from http://ies.ed.gov/ncee/wwc/pdf/essig.pdf Wilkinson, L. & APA Task Force on Statistical Inference. (1999). Statistical methods in psychology journals: Guidelines and explanations. American Psychologist, 54 (8) 594 - 604. Retrieved March 14, 2010 from http://www.loyola.edu/library/ref/articles/Wilkinson.pdf |
[ p. 27 ]
|
Further reading: Angoff, W. H. (1971, 1984). Scales, norms, and equivalent scores. In R. L. Thorndike (Ed.), Educational measurement (2nd ed.) (pp. 508-600). Washington, DC: American Council on Education. Retrieved on March 14, 2010 from http://www.ets.org/portal/site/ets/menuitem.c988ba0e5dd572bada20bc47c39215 09/ ?vgnextoid=78c5c2f348b46010VgnVCM10000022f95190RCRD&vgnextchannel=dcb3be3a864f4010VgnVCM10000022f95190RCRD Byham. W. C. (1970, July/August). Assessment centers for spotting future managers. Harvard Business Review, 59, 150-167 Cizek, G. J. & Bunch, M. B. (Eds.) (2007). Standard Setting: A Guide to Establishing and Evaluating Performance Standards on Tests (New Edition). Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage Publications. Cross, L. H., Impara, J. C., & Frary, R. B. (1984). A comparison of three methods for establishing the minimum standards on the national teacher examinations. Journal of Educational Measurement, 21 (2) 113-129. George, S. George, Haque, M. S. & Oyebode, F. (2006) Standard setting: Comparison of two methods. BMC Medical Education 6 (46). DOI: 10.1186/1472-6920-6-46 Kaftandjieva, F. (2009). Basket Procedure: The breadbasket or the basket case of standard setting methods? In N. Figueras & J. Noijons (Eds.) Linking to the CEFR levels: Research perspectives. (pp. 21-34). Arnheim: CITO/ EALTA. Retrieved March 11, 2010 from http://www.coe.int/t/dg4/linguistic/EALTA_PublicatieColloquium2009.pdf Rock, D. A., Davies, E. L., & Werts, C. (1980). An empirical comparison of judgmental approaches to standard setting procedures (Research report #0-7). Princeton, NJ: Educational Testing Service. |
[ p. 28 ]
3 Q: What is the university entrance exam item below probably attempting to measure? How could this item be improved?
|
Further reading: Bothell, T. W. (2001) 14 rules for writing multiple-choice questions. Retrieved on March 20, 2010 from http://testing.byu.edu/.../14%20Rules%20for%20Writing%20Multiple-Choice%20Questions.pdf Christensen, C. A. (2005). The role of orthographic-motor integration in the production of creative and well-structured written text for students in secondary school. Educational Psychology, 25 (5) 441 - 453 DOI: 10.1080/01443410500042076 [ p. 28 ] Gray, R. (2004). Grammar correction in ESL/EFL writing classes may not be effective. The Internet TESL Journal, 10 (11). Retrieved on March 15, 2010 from http://iteslj.org/Techniques/Gray-WritingCorrection.htmlHaladyna, T. M., Downing, S. M., & Rodriguez, M. C. (2002). A review of multiple-choice item-writing guidelines for classroom assessment. Applied Measurement in Education, 15 (3), 309 - 334. Kehoe, J. (1995). Writing multiple-choice test items. Practical Assessment, Research & Evaluation, 4 (9). Retrieved March 20, 2010 from http://PAREonline.net/getvn.asp?v=4&n=9 . This paper has been viewed 80,293 times since 11/13/1999. Truscott, J. (1996). The case against grammar correction in L2 writing classes. Language Learning 46 (2) 327-369. Retrieved on March 15, 2010 from http://hss.nthu.edu.tw/~fl/faculty/John/Grammar_ Correction_in_L2_Writing_Class.pdf |


[ p. 30 ]
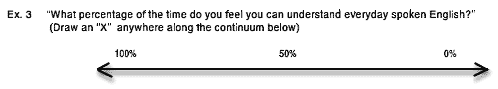
|
Further reading: Draper, S. W. (2009, December 23). The Hawthorne, Pygmalion, Placebo and other effects of expectation: Some notes. Retrieved on March 15, 2010 from http://www.psy.gla.ac.uk/~steve/hawth.html#Preface Jones, R. A. (1981). Self-fulfilling Prophecies: Social, Psychological, and Physiological Effects of Expectancies. Hillsdale, NJ: Psychology Press. Mizumoto, A., & Takeuchi, O. (2009). Comparing frequency and trueness scale descriptors in a Likert scale questionnaire on language learning strategies. JLTA Journal, 12, 116 - 130. Van Bennekom, F. (2007). How Question Format Affects Survey Analysis. Retrieved on March 16, 2010 from http://www.greatbrook.com/survey_question.htm Zdep, S. M. & Irvine, S. H. (1970). A reverse Hawthorne effect in educational evaluation. Journal of School Psychology 8, 85 - 95. |
[ p. 31 ]
Further reading:
|
|
Further reading: Marczyk, G., DeMatteo, D., & Festinger, D. (2005). Essentials of research design and methodology. New York: John Wiley & Sons. Marion, R. (2004). The Whole Art of Deduction: Defining Variables and Formulating Hypotheses. Retrieve March 27, 2010 from http://sahs.utmb.edu/pellinore/intro_to_research/wad/vars_hyp.htm |
[ p. 33 ]
|
Further reading: Genesee, F. & Upshur , J. A. (1996). Classroom-Based Evaluation in Second Language Education (Cambridge Language Education). New York: Cambridge University Press. Test Rubric: Problems Associated with Rubrics. (2002). In S. A. Mousavi. An Encyclopedic Dictionary of Language Testing. (3rd Ed.). (pp. 755-757). Taipei: Tung Hua Book Company. |
[ p. 34 ]
A: The correct answer is (B). In truncation, the extreme top and/or bottom scores of a test are removed from consideration. Truncation may also occur if the observation period is shorter than the events under investigation, such as in a mortality study.|
Further reading: Mandel, M. (2007). Censoring and truncation - Highlighting the differences. The American Statistician, 61 (4) 321 - 324. DOI: 10.1198/000313007X247049. |
|
Acknowledgements Many thanks to Lars Molloy, Ed Schaeffer, and Chris Weaver for feedback on this article. The responsibility for any errors herein rests with the author. |
[ p. 35 ]